Understanding what shapes dental-implant pricing helps you budget with confidence and avoid misleading quotes. The total cost can vary widely depending on your oral-health needs, materials, and the provider’s experience.
At Care Dental Center, we explain every factor—technology and number of implants—so you understand how each step affects cost and outcome. We also clarify any preparatory care involved. Transparent planning lets you make decisions that fit your goals and comfort level.
This guide breaks down the elements that influence implant pricing, from surgical complexity to financing options, and shows how informed choices can make advanced tooth replacement more affordable near you.
Key Takeaways
Implant price hinges on how many teeth you replace and the work needed.
Material choice, implant components, and extra procedures drive costs.
Location, clinic type, and payment options shape your final out-of-pocket amount.
Key Factors That Influence Dental Implant Cost
Several clear things drive the price you’ll pay: how many implants you need, which surgical approach your mouth requires, any bone or tooth work before surgery, and who performs the treatment. These points affect the number of visits, the length of treatment, and the type of materials used.
Number of Implants Needed
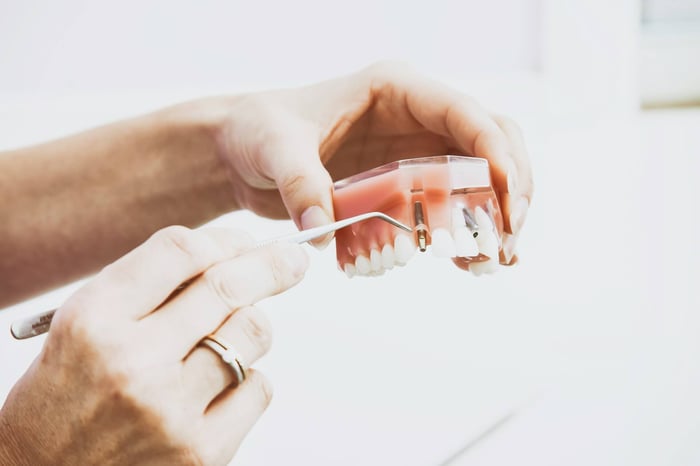
The cost rises with each implant. A single tooth implant includes the implant, abutment, and crown. If you need multiple implants, some clinics offer package discounts, but the total still increases.
Full-arch restorations like All-on-4 or full-mouth implants place fewer implants per arch than individual crowns, so the per-tooth cost can be lower. Zygomatic implants follow a different pricing path because they anchor in the cheekbone and require specialized surgery.
Expect higher lab and material costs, longer surgery time, and more follow-up visits with each added implant. Also factor in possible extra abutments or temporary prostheses during osseointegration waiting periods.
Type of Dental Implant Procedure
Different procedures change the price. A routine implant placement by an implant dentist or general dentist is usually cheaper than complex surgery by an oral surgeon or periodontist.
Single tooth implant cases are straightforward when bone and gum health are good. Full-mouth implants or full-arch restorations, including All-on-4, need more planning, imaging, and longer operating-room time. Zygomatic implants, sinus lifts, or cases requiring guided surgery or CAD/CAM prosthetics cost more.
Materials matter too. Titanium implants are common and cost-effective. Zirconia implants and premium branded systems often carry higher fees. Ask about the implant brand and crown material when comparing quotes.
Pre-Implant Procedures and Preparations
Pre-treatment work can add a high cost. Tooth extraction, bone grafting, and sinus lifts are common before implant placement. If you lack sufficient jawbone, bone grafting or a sinus lift may be essential for stable implant placement.
These procedures require extra surgery time, graft material costs, and healing time before the implant can be placed. That lengthens the treatment timeline and the number of follow-up visits during osseointegration.
You may need 3D imaging, CBCT scans, and diagnostic planning before any surgical step. Those imaging and planning fees are separate on many estimates, so ask for a full cost breakdown that includes scans, temporary crowns, and follow-up care.
Dentist's Experience and Credentials
Who places your implant matters for both outcome and price. An oral surgeon or periodontist with advanced implant training typically charges more than a general dentist. Implant centers and specialist clinics may charge premium fees for their experience and equipment.
More experienced providers often use advanced techniques, handle complex cases like zygomatic implants or full-mouth implants, and offer better-managed treatment plans. That can reduce complication risks but raise the initial cost.
Look for providers near you who list credentials, case examples, and patient reviews. Ask whether the implant dentist works with a lab that handles the prosthetic stages, and how many follow-up visits are included in the price.
Impact of Materials and Implant Components on Pricing
Material choices and component types directly change what you pay. Some parts cost more because they last longer, look better, or need special fittings.
Material Quality and Biocompatibility Matter
The metal or ceramic used in an implant post affects both comfort and durability. According to Harvard Health Publishing, titanium remains the gold standard for its strength and bone integration, while zirconia offers an alternative for patients sensitive to metals but at a higher price.
Implant Post Materials: Titanium vs Zirconia
Titanium implants are the most common and usually cost less than zirconia implants. Titanium posts bond well with bone and have decades of research backing their success. If you choose a titanium implant post, you often save on the implant itself and on repairs later.
Zirconia implants cost more up front. They are metal-free and can look better for patients with thin gums or metal sensitivities. Zirconia is more brittle than titanium, so your dentist may prefer titanium for back teeth that take heavy chewing forces.
Your jawbone quality can also affect the choice. Poor bone may need grafting, which raises the total price regardless of the post material.
Abutment and Crown Choices
Abutments connect the implant post to the implant crown. Stock titanium abutments are cheaper and widely available. Custom abutments—made from titanium or zirconia—fit better and can improve gum shape, but they raise the cost.
Crown material matters too. Porcelain-fused-to-metal crowns are affordable and durable. All-ceramic or zirconia crowns cost more but give a more natural look. If you want a high-transparency crown for a front tooth, expect higher lab fees.
Your dentist will quote abutment and crown costs separately. Ask for options and lab warranties to compare value, not just price.
Additional Components (Screws, Connectors, etc.)
Small parts like implant screws, healing caps, and connectors add to the bill. A standard titanium implant screw is inexpensive, but specialized screw-retained systems or gold-plated screws will cost more.
Connector systems (for overdentures or multi-unit bridges) also vary in price. Simple ball attachments are cheaper. Multi-unit connectors for All-on-4 style restorations use precise machining and increase lab and component fees.
If a component needs custom machining or a proprietary brand part, replacement and repair costs rise later. Ask your provider which parts they use and if spare parts are easy to get in your area.
Location, Clinic Type, and Diagnostic Costs
Your choice of city, clinic, and scans will shape the price you pay. Expect prices to change with local living costs, whether you pick a dental implant center or a general dentist, and which diagnostic tests (like a CBCT scan) the clinic uses.
Regional and Local Cost Variations
Where you live affects the cost of a dental implant more than you might expect. Big cities and coastal areas usually have higher rents and wages, so a single implant often costs more there than in smaller towns.
For example, clinics in major metro areas may charge enough that the cost of a dental implant rises by 20–40% versus suburban or rural practices. Competition also matters.
If you search “dentist near me” in a dense market, you can compare several quotes and find lower prices or bundled offers. Travel can save money: some patients pick an implant center in a nearby city with lower fees and schedule a single trip for surgery and follow-ups.
Clinic Setting: Specialist Centers vs General Practices
You’ll see two main clinic types: implant centers and general dental practices. An implant center or dental implant center focuses on implants and often hires oral surgeons and prosthodontists. They charge more for expertise and advanced workflows, but may reduce complication risk.
A general dentist can place implants, too, usually at a lower fee. That can work if your case is straightforward.
Consider the complexity of your situation: bone grafting, sinus lifts, or full-arch work typically benefits from a specialist. Ask each clinic to itemize the cost of surgery, the abutment, and the final crown so you can compare real value, not just a headline price.
Diagnostics and Imaging Fees
Diagnostics add clear, upfront costs but improve safety and planning. A 2D X-ray costs less, while a CBCT scan gives 3D images of bone, nerves, and sinuses. Many implant centers include CBCT in the implant estimate; other clinics bill it separately.
Expect a CBCT to add a few hundred dollars to the total. Also, check whether the clinic uses digital planning or guided surgery. Those services can add lab and software fees, but can shorten surgery time and improve implant position.
When you ask “how much is a dental implant,” request an itemized quote listing imaging (CBCT), surgical fees, implant post, abutment, and crown. That helps you compare offers from a nearby dentist or a specialized implant center without guessing what’s included.
Dental Insurance, Financing, and Payment Factors
Costs for implants vary by what your plan covers, how much you must pay first, and which financing choices you use. Knowing your insurance limits, deductible, and required approvals helps you estimate how much dental implants will actually cost you.
Dental Insurance Coverage and Limitations
Most dental plans treat implants as elective and may not cover the implant fixture itself. Some plans will cover the implant crown or parts of the restoration, while others cover nothing. Check your policy language and ask your insurer whether they list “dental implants,” “implant crowns,” or “prosthodontics” as covered services.
If you have medical reasons (trauma or disease), your medical insurer might cover some costs. Confirm network rules, too: an in-network dentist often has negotiated rates that lower your bill. Get a written benefits summary from your insurer so you know exactly what they will pay.
Deductibles and Out-of-Pocket Costs
Your deductible is the amount you must pay before insurance contributes. Many dental plans have annual deductibles of $50–$200 for major procedures, but limits vary. Even after meeting the deductible, insurers often pay a percentage (e.g., 50% for major work) and you pay the rest.
Watch for annual maximums. Typical dental plan yearly caps range from $1,000–$2,000. If implant treatment exceeds that cap, you’ll cover the balance. Ask your dentist for a full treatment estimate and a breakdown of what you’ll owe after deductible and coinsurance.
Financing Options and Payment Plans
Dental offices commonly offer in-house payment plans that split costs over several months. These plans can be interest-free for short terms (3–12 months) or have low interest for longer terms. You can also use third-party medical lenders, credit cards, or healthcare credit lines like CareCredit.
Compare total cost, interest rate, and monthly payment before signing. Ask the office for several plan options and for a written schedule of payments. If you expect the surgery to be complex (bone grafts, sinus lifts), include those costs when comparing plans so your monthly amount is accurate.
Pre-Authorization and Coverage Requirements
Pre-authorization (pre-approval) is a formal insurer review that confirms coverage before treatment. Your dentist submits a treatment plan, X-rays, and a cost estimate. Approval can reduce surprises by showing what portion the insurer will pay.
Insurers may require documentation that implants are medically necessary. They can also require waiting periods or deny coverage if prior treatment alternatives were not tried. Start pre-authorization early and follow up in writing.
Keep copies of all submissions and approvals for your records so you can resolve disputes if they arise.
Planning Your Implant Treatment With Confidence
Dental-implant pricing depends on many moving parts—materials, surgical skill, and necessary preparatory care. Knowing these variables upfront helps you balance quality, value, and long-term results.
At Care Dental Center, we combine precise imaging, advanced materials, and clear communication so patients understand every cost before treatment begins. Our transparent process supports predictable outcomes and lasting comfort.
If you’re researching implant options or comparing quotes, schedule a consultation today for honest guidance, detailed estimates, and gentle, patient-focused care designed to fit your smile and budget.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section explains what changes local implant prices, the role of implant types and materials, how provider skill affects fees, extra procedures that add cost, common payment options, and insurance rules you should check.
What determines the price of dental implants in my area?
Local clinic overhead, lab fees, and supply costs set a baseline. Regional demand and competition also change prices from town to town. The specific implant system, crown material, and any imaging (CBCT vs. X-ray) raise or lower the final number. Ask for an itemized estimate so you can see each charge.
Are there different types of dental implants, and do they vary in cost?
Yes. Titanium implants are common and usually cost less than zirconia. Some branded implant systems carry a premium for design or warranty. Crowns and abutments come in materials like PFM, zirconia, or lithium disilicate, which affects lab fees. Custom abutments and high-end crowns increase the total cost.
How does the experience of the dentist affect implant pricing?
Dentists with advanced implant training or long experience often charge more. You may pay more upfront for lower risk and fewer complications. Specialists like oral surgeons or periodontists can bill differently than general dentists. Compare provider outcomes, not just the price.